How math and stats are changing the way of doing financial trading.

Spectacular successes and failures, high volumes of orders sent in fractions of seconds, huge quantity of money raised in few hours. There is no doubt that quantitative trading today casts a huge shadow in the financial market. In this series of articles, it is my inspiration to explain what quantitative trading is about in a simple and intuitive manner. There will be no equations and the use of technical terms will be limited to the maximum.
Let’s start with a definition: quantitative trading can be defined as the systematic implementation of trading strategies that humans create through rigorous research. The people behind the quantitative strategies are called quantitative traders or simply quants.
There are two things I’d like to underline about the definition I have just given. First, quant trading is systematic. It is a rigorous discipline made by methodology and established approaches. Second, it requires rigorous research. It is quite impossible to became a good quant trader without an hard training. Have a mathematical background is not enough. If you do not know core concepts such as risk management and position sizing, your destiny is to lose money.
There is a concept that I’d like you always keep in mind when we talk about quantitative trading: is people and not the machines responsible for the many interesting and criticized aspects of quantitative trading.
High Frequency Trading (HFT) is a subset of Algorithmic Trading. It observes information and market parameters and generates trading decisions automatically without any human action. The HFT are very populare in Financial Market makes money in 95% of cases. They can not accommodate large investments because the opportunities they seek are small and fleeting.
A term that you can hear often in the context of quantitative trading is black box. In a nutshell, the black boxes are quantitative trading strategies. The goal of a black box is to find an optimal balance between profits, limiting of risks and cost associated with trading, thereby determining the best portfolio.
What makes them so famous is the fact that they are highly sophisticated. Their implementations require skills in mathematics and statistics, as well as a deep understanding of the dynamics inside the financial market.
Black boxes are surrounded by a general idea of opacity which makes them particularly hard to understand for the people which is not involved in quantitative trading. In particular, there are two adjectives that are massively used in the literature to describe a black box: complex and secret.
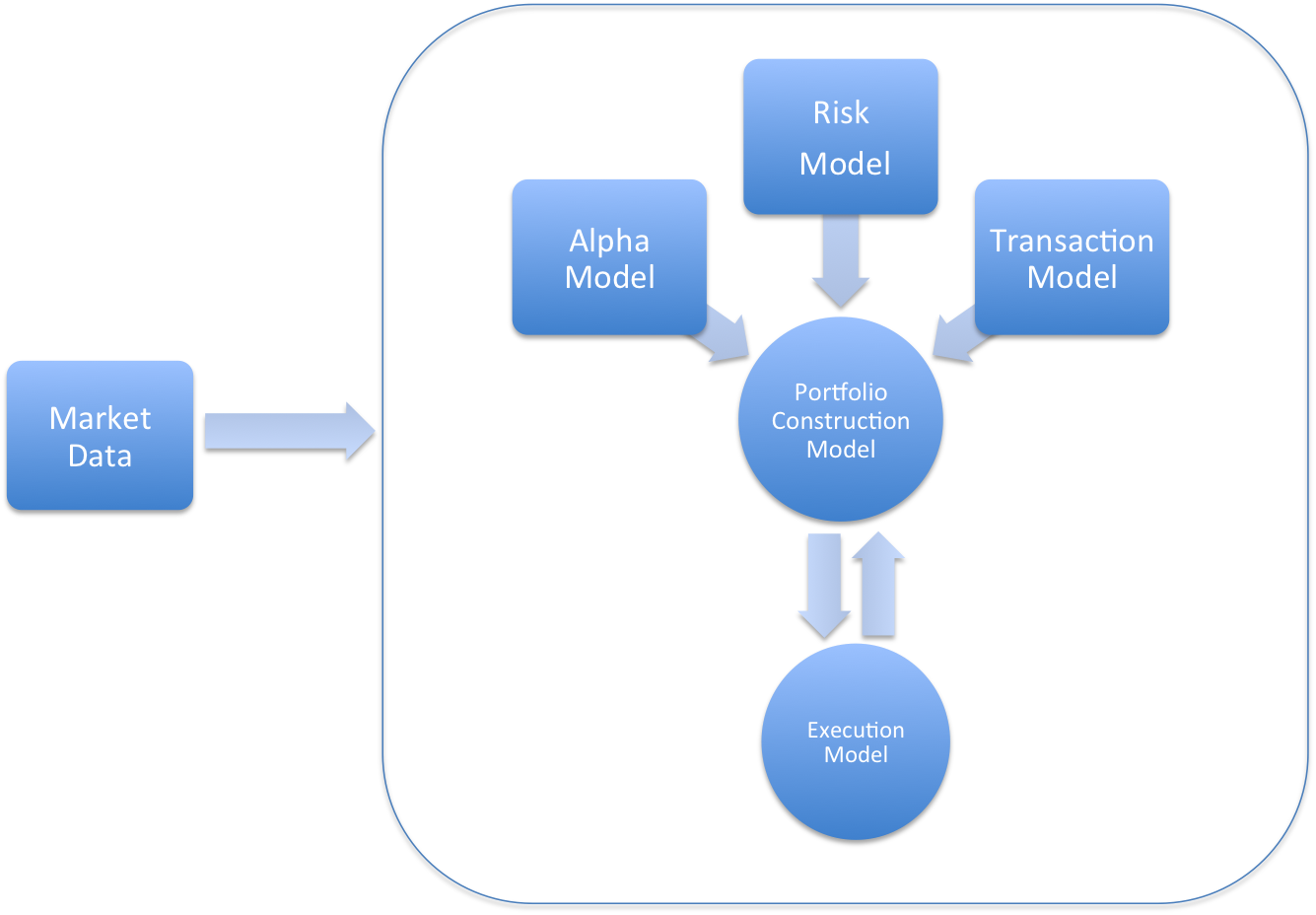
######Black Box structure, credits ‘Inside The Black Box’ by Rishi Narrang
A quant use systematically an alpha-seeking investment strategy that has been specified on the basis of an exhaustive search. An alpha investment strategy tries to get returns regardless of the market direction. Some of the most used techniques are pairs trade and statistical arbitrage. They are both based on the same assumption: two similar financial instruments (e.g. stocks about IT companies which sell Cloud) behave similarly.
A positive aspect about quants is that they have a systematic approach to problem solving. They are naturally predisposed to conduct any type of measurement, including risk. Quants use data from the market that are the input of a searching process to determine if their ideas are right or not during the course of time. When you arrive at a strategy sufficiently good and satisfactory, they implement the strategy in a “quant system”. This means that the emotional component is kept out of the decision making process which is at the base of trading and investments in general, and imposes a discipline based on ideas that have been tested.
In the next post we’ll talk deeply about every blocks which a Black Box is made up:
- Alpha model
- Risk model
- Transaction Cost model
- Portfolio Construction model
- Execution model
###Further Information
Inside the Black Box: The Simple Truth About Quantitative Trading by Rishi K. Narang